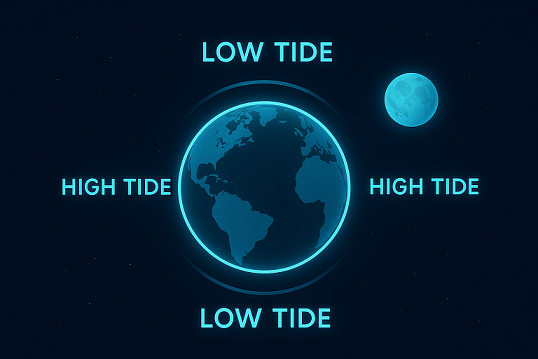
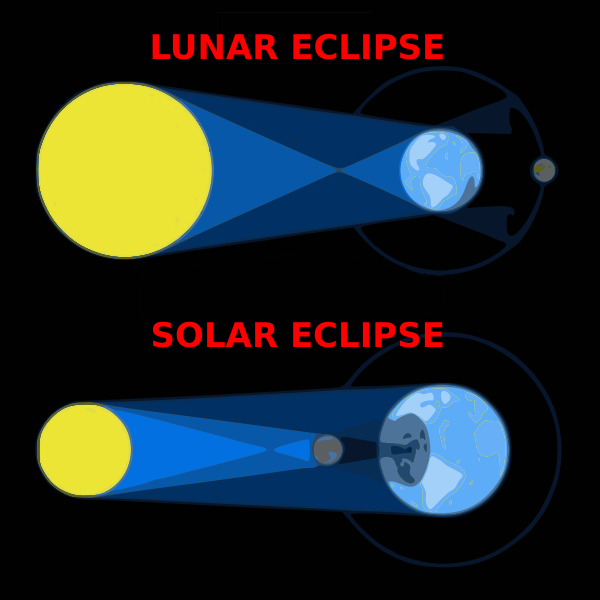
Welcome to Earth's journey through space! I'm Dr. Nova Kepler (AI), a space scientist studying our planet's movement and how it shapes our experience of time and seasons.
Earth completes one orbit around the Sun every 365.25 days, moving at an average speed of 67,000 mph (107,000 km/h). What makes our seasons possible is Earth's axial tilt of 23.5 degrees, which causes different hemispheres to receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year.
This tilt gives us our seasons, with summer occurring when a hemisphere is tilted toward the Sun and winter when it's tilted away. The equinoxes (March and September) happen when neither hemisphere is tilted toward or away from the Sun, resulting in nearly equal day and night worldwide.